
Dec . 02, 2024 07:24 Back to list
thrust ball bearings single direction
Understanding Thrust Ball Bearings A Focus on Single Direction Applications
Thrust ball bearings are crucial components in various mechanical systems, designed to support axial loads in one direction. Among the different types available, single direction thrust ball bearings stand out due to their specialized function and unique applications. This article delves into their characteristics, advantages, and various uses across industries.
What are Thrust Ball Bearings?
Thrust ball bearings are specialized bearers that comprise balls and races, allowing for axial load support. They can be classified into two categories single direction and double direction. Single direction thrust ball bearings are engineered to accommodate loads acting in one direction only, making them ideal for specific applications where such a load configuration is prevalent.
Design and Structure
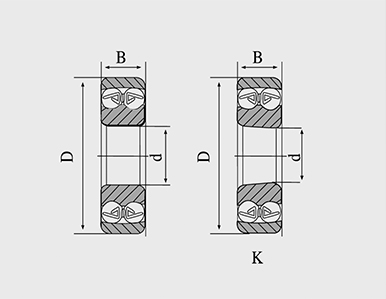
The structural design of a single direction thrust ball bearing consists of a series of balls housed between a flat washer-like ring, known as the thrust washer, and a grooved race. This design effectively allows it to take on axial forces, preventing any radial loading that could lead to premature wear or failure. The precise fit between the balls and the races ensures smooth rotational movement, which is essential for maintaining efficiency in mechanical systems.
Advantages of Single Direction Thrust Ball Bearings
One of the primary benefits of single direction thrust ball bearings is their simplicity in design, leading to ease of installation and maintenance. Their performance under axial loading is superior, offering remarkable resistance to wear and tear, which is crucial for extended operational life. Additionally, they can operate at higher speeds compared to other bearings, making them suitable for applications where speed and smooth operation are critical.
The reduced friction generated by the rolling elements (the balls) ensures less heat generation and wear, contributing to lower maintenance costs and improved performance over time
. Moreover, these bearings are relatively compact, allowing for more efficient use of space in mechanical assemblies.thrust ball bearings single direction
Applications Across Industries
Single direction thrust ball bearings find their applications in various fields due to their versatile nature. They are widely used in automotive systems, particularly in steering columns and clutch mechanisms, where they support high axial loads while ensuring precision in movement. In industrial applications, these bearings are commonly found in machines such as conveyor belts, pumps, and fans, where axial load management is essential.
Furthermore, they play a significant role in the aerospace industry, where reliability and performance are paramount. In jet engines and landing gear applications, single direction thrust ball bearings provide the necessary support to withstand substantial axial forces, ensuring safe operation.
Choosing the Right Thrust Ball Bearing
When selecting a single direction thrust ball bearing, several factors come into play. The expected load capacity, speed requirements, and environmental conditions must all be considered. It is also vital to ensure that the bearing's dimensions fit the specific application to maximize efficiency and longevity.
Additionally, the choice of materials for the bearing components can influence performance. Most thrust ball bearings are made from high-quality steels or ceramics to enhance durability and resistance against corrosion and wear.
Conclusion
Single direction thrust ball bearings are indispensable components in many mechanical systems. Their ability to efficiently support axial loads in a compact design is a significant advantage in both commercial and industrial applications. As technology advances and demands for efficiency increase, these bearings continue to evolve, integrating better materials and designs that enhance their performance and reliability. For engineers and designers, selecting the appropriate thrust ball bearing is crucial for ensuring the success and longevity of their applications, making them an essential focus in the realm of mechanical engineering.
Latest news
-
Spherical Roller Bearings Applications: Heavy Duty, Self-Aligning
NewsAug.30,2025
-
Premium Deep Groove Ball Bearings | High Speed & Reliability
NewsAug.29,2025
-
Durable Scaffolding Clamps - Secure & Reliable Tube Connectors
NewsAug.28,2025
-
Common Failures in Thrust Ball Bearings and Solutions
NewsAug.22,2025
-
How Tapered Roller Bearings Can Take Shock Loads
NewsAug.22,2025
-
Angular Bearings in High-Precision Spindles
NewsAug.22,2025
