
Aug . 11, 2024 04:42 Back to list
Various Types of Thrust Ball Bearings and Their Applications in Mechanical Engineering
Thrust Ball Bearing Types
Thrust ball bearings are specialized types of bearings designed to accommodate axial loads, meaning they can handle forces that are directed along the shaft. These bearings are typically used in applications where the direction of the load is primarily vertical or horizontal with respect to the axle. There are various types of thrust ball bearings, each tailored for specific applications and operational requirements. This article explores the most common types and their characteristics.
1. Single Direction Thrust Ball Bearings
Single direction thrust ball bearings consist of a shaft washer, a housing washer, and a ball complement. They are designed to support axial loads in only one direction. This makes them ideal for rotary applications where the load is consistently applied in one direction. Common usages include automotive applications and various industrial machines, where they help manage the axial positioning of components.
These bearings are relatively simple in design, making them easy to install and maintain. However, it’s crucial to ensure that they are used correctly to prevent damage, as applying loads in the opposite direction can lead to failure.
2. Double Direction Thrust Ball Bearings
As the name suggests, double direction thrust ball bearings can accommodate axial loads from two directions. This design incorporates two sets of balls and two housing washers, allowing it to handle loads that may change direction during operation. These bearings are particularly useful in applications involving oscillating motions or variable load directions, such as in some machine tools or in rotating assemblies used in heavy machinery.
The advantage of double direction thrust bearings is their versatility; they can adjust to varying load conditions without the need for additional components. However, they may also require more maintenance due to their complexity in construction.
thrust ball bearing types
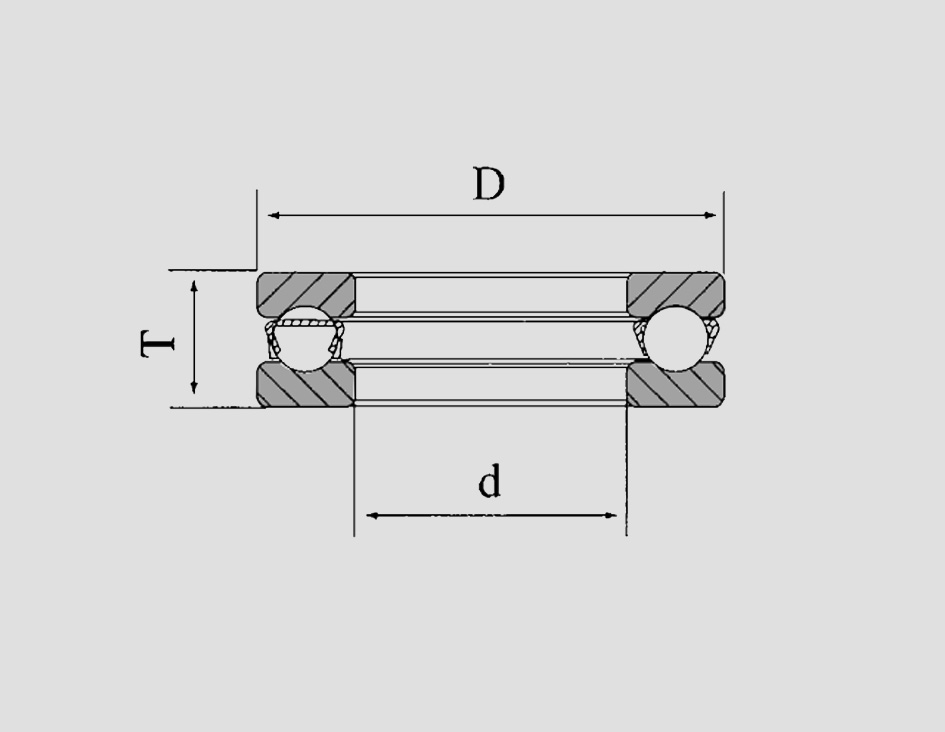
3. Thrust Ball Bearings with Spherical Raceways
Another specialized type is thrust ball bearings with spherical raceways. These bearings are designed to accommodate misalignment between the shaft and housing, allowing for greater flexibility in performance. The spherical nature of the raceway permits a certain degree of angular misalignment, which can be beneficial in applications where perfect alignment cannot be guaranteed.
These bearings are often found in applications where equipment may experience shifts due to temperature changes or operational vibrations. They provide a smoother operation and longer service life because they can handle misalignment without excessive wear.
4. Miniature Thrust Ball Bearings
Miniature thrust ball bearings are a smaller version of standard thrust ball bearings. They are designed for compact applications where space is a constraint, such as in electronic devices, small motors, and various hand-held tools. Despite their size, they can support significant axial loads relative to their dimension, making them highly efficient in small-scale applications.
These miniature versions require precision in manufacturing and assembly, as even small inaccuracies can lead to failure due to the tight tolerances involved.
Conclusion
Thrust ball bearings play a pivotal role in various mechanical applications where axial loads are present. Understanding the different types of thrust ball bearings—single direction, double direction, those with spherical raceways, and miniature versions—enables engineers and technicians to choose the appropriate bearing for their needs. Each type has its unique benefits and considerations, and selection should be based on factors such as load direction, alignment requirements, and space constraints. Proper understanding and application of these bearings ensure improved efficiency, reliability, and longevity of machinery and equipment. As technology advances, we can expect further innovations in bearing design and materials, leading to even more specialized thrust ball bearings.
Latest news
-
Industrial Machine Bearings: the core hub of mechanical operation
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Deep Groove Ball Bearing: A Dynamic "Elf" Operating Mechanically
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Compact craftsmanship: the way to optimize the space of Concrete Mixer Bearings
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Combine Harvester Bearings: The 'Steel Backbone' of Modern Agriculture
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Bearing Machinery: a flexible support hub for mechanical operation
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Agricultural Equipment Bearings: A Power Hub for Intensive Cultivation under Radial Space Constraints
NewsAug.06,2025
