
Jul . 27, 2024 08:21 Back to list
Understanding the Nomenclature and Designation of Tapered Roller Bearings for Various Applications
Understanding Taper Roller Bearing Nomenclature
Taper roller bearings are a crucial component in many mechanical systems, providing the ability to handle both radial and axial loads. Their design allows for effective load distribution, making them ideal for heavy machinery and automotive applications. To fully appreciate their functionality and application, it’s essential to understand the nomenclature associated with taper roller bearings.
Components of Taper Roller Bearings
Taper roller bearings consist of several key components the inner ring (cone), outer ring (cup), rolling elements (tapered rollers), and cage. The inner ring has a tapered raceway, which allows the rollers to make contact at a specific angle. This angular contact enables taper roller bearings to manage higher loads than other bearing types, such as spherical or cylindrical roller bearings.
The nomenclature of taper roller bearings typically includes a code that conveys essential information about the bearing's dimensions and capabilities. This code is standardized by the American Bearing Manufacturers Association (ABMA) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Breakdown of Bearing Nomenclature
1. Basic Designation The basic designation comprises a combination of letters and numbers that identify the type and series of the bearing. For instance, the designation 32005 breaks down as follows - The 32 indicates the series, which corresponds to a specific size range of taper roller bearings. - The 005 part denotes the bearing’s dimensions, specifically the width and the cone diameter.
taper roller bearing nomenclature
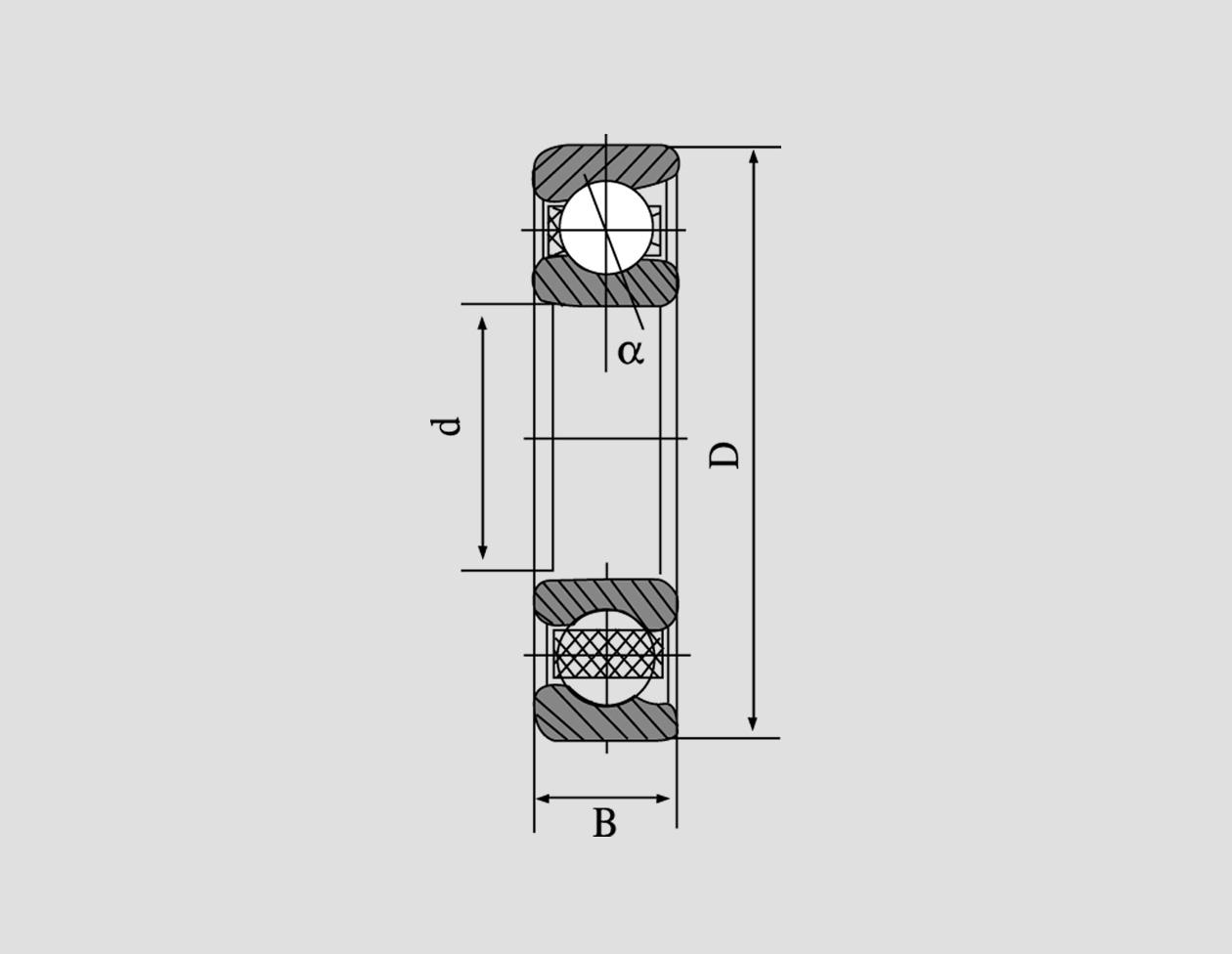
2. Suffix Codes Following the basic designation, there can be suffix codes that provide additional information. For example, a suffix A might indicate a matched pair of bearings, while B signifies a metric dimension. It is important to refer to the manufacturer's specifications to understand each suffix's specific meaning, as they can vary.
3. Load Ratings Taper roller bearings are also identified by their dynamic and static load ratings, which are usually expressed in kilonewtons (kN). The dynamic load rating, denoted as C, refers to the maximum load the bearing can continuously withstand while rotating, while the static load rating, denoted as C0, indicates the maximum load it can support while stationary.
4. Clearance and Fit Taper roller bearings may have additional identifiers for clearance classes (e.g., C3 for increased clearance) and tolerance classes that determine the fit of the components. These parameters are vital for ensuring optimal performance in applications with specific temperature and operational demands.
Importance of Nomenclature
Understanding the nomenclature of taper roller bearings is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it enables engineers and technicians to select the right bearing for specific applications, ensuring compatibility and efficiency. Secondly, it facilitates communication between manufacturers, suppliers, and customers, reducing the likelihood of errors in ordering parts. Lastly, it aids in maintaining and servicing machinery, as technicians will need to identify the correct bearings to replace or adjust based on the nomenclature.
Conclusion
In summary, the nomenclature of taper roller bearings provides a systematic way of identifying and specifying these critical components in various mechanical systems. By familiarizing oneself with the basic designation, suffix codes, load ratings, and clearance specifications, one can effectively navigate the complexities of bearing selection and maintenance. As industries continue to evolve and require more sophisticated machinery, a thorough understanding of taper roller bearing nomenclature will remain a vital skill for engineers and technicians alike.
Latest news
-
Grooved Ball Bearing Design and Functionality
NewsJun.04,2025
-
Concrete Mixer Bearing Load Capacity Testing
NewsJun.04,2025
-
6004 Bearing Dimensions in Robotic Joint Designs
NewsJun.04,2025
-
Advantages of Single-Row Deep Groove Ball Bearings
NewsJun.04,2025
-
Applications of Deep Groove Ball Bearings in Automotive Systems
NewsJun.04,2025
-
Innovations in Bearing Pressing Machine Design
NewsJun.04,2025
