
Aug . 13, 2024 01:14 Back to list
Understanding the Functionality and Applications of Tapered Roller Bearings in Mechanical Systems
Understanding Tapered Roller Bearings Design and Applications
A tapered roller bearing is an essential component used in various mechanical applications, particularly in areas requiring the support of heavy radial and axial loads. Recognized for their unique design, tapered roller bearings facilitate motion and contribute significantly to the efficiency and reliability of machines. This article will delve into the design features, operational principles, and applications of tapered roller bearings.
Design Features
Tapered roller bearings consist of an inner ring, an outer ring, tapered rollers, and a cage. The components are designed such that the rollers maintain contact at a single line, which means the rollers can handle both radial and axial loads simultaneously. The tapered shape of the rollers permits them to roll smoothly along the conical surfaces of the inner and outer rings, thereby reducing friction and wear.
One of the key aspects of tapered roller bearings is their ability to accommodate misalignments. The conical shapes allow some degree of movement, which can be beneficial in applications where components may not be perfectly aligned. This feature enhances the overall durability and reliability of the bearing under various working conditions.
Operational Principles
Tapered roller bearings operate on the principle of load distribution. When a load is applied, the roller's contact line changes based on the direction of the load. This design allows for the separation of the load into its radial and axial components, enabling the bearing to support heavy loads efficiently.
a tapered roller bearing has
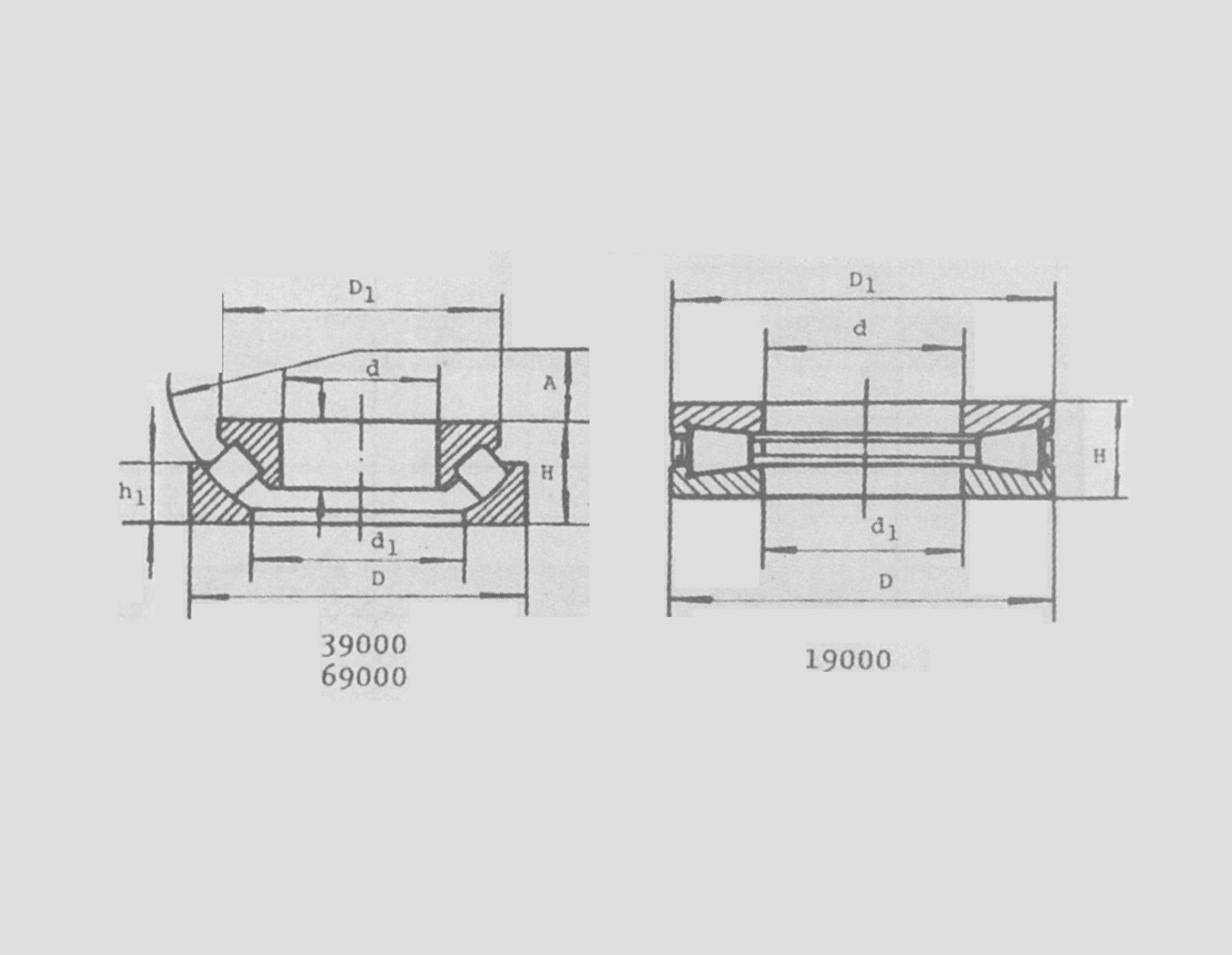
The internal geometry of tapered roller bearings also plays a crucial role in their performance. The angle and length of the tapered rollers, along with the contact angle of the bearing, contribute to their load-carrying capabilities. Typically, a larger contact angle increases the axial load capacity, which is why engineers consider these factors when designing systems that require specific load-handling characteristics.
Applications
Tapered roller bearings find use in a diverse range of industries and applications. One of the most common applications is in automotive wheel hubs, where they support the vehicle’s weight while allowing for smooth wheel rotation. In addition, they are frequently employed in industrial equipment, such as conveyor systems, gearboxes, and machine tools, to reduce friction and improve operational reliability.
In energy applications, such as wind turbines, tapered roller bearings are essential for supporting rotating components while withstanding significant axial and radial stresses. Moreover, they are also used in railways and heavy-load machines, where their robust design can absorb significant shocks and vibrations.
Maintenance and Durability
To ensure the longevity and proper functioning of tapered roller bearings, routine maintenance is essential. Factors such as lubrication, temperature control, and monitoring for wear can significantly affect the lifespan of the bearings. Regular inspections can help detect early signs of damage or wear, allowing for timely replacements and reducing the risk of catastrophic failure in machinery.
In conclusion, tapered roller bearings are vital components in various mechanical systems, engineered to support heavy loads while ensuring smooth operation. Their unique design and construction make them suitable for countless applications across multiple industries. Understanding their principles and features can help engineers and technicians optimize equipment performance, leading to enhanced efficiency and a reduced risk of downtime. As technology advances, the demand for specialized tapered roller bearings will likely increase, paving the way for innovations in their design and applications.
Latest news
-
Industrial Machine Bearings: the core hub of mechanical operation
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Deep Groove Ball Bearing: A Dynamic "Elf" Operating Mechanically
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Compact craftsmanship: the way to optimize the space of Concrete Mixer Bearings
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Combine Harvester Bearings: The 'Steel Backbone' of Modern Agriculture
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Bearing Machinery: a flexible support hub for mechanical operation
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Agricultural Equipment Bearings: A Power Hub for Intensive Cultivation under Radial Space Constraints
NewsAug.06,2025
