
Sep . 08, 2024 08:55 Back to list
Tapered Thrust Bearing - Enhanced Load Support and Stability
Understanding Tapered Thrust Bearings Design and Applications
Tapered thrust bearings are a specific type of bearing designed to handle axial loads in various applications. They are distinguished by their tapered shape, which allows for the efficient distribution of forces within machinery. This article explores the design, functionality, and applications of tapered thrust bearings, providing insight into why they are essential in many engineering fields.
Design and Structure
Tapered thrust bearings consist of two main components the raceway and the tapered rolling elements (usually tapered rollers). The raceway is made up of two conical surfaces; one is stationary while the other rotates. The rollers are positioned between these two surfaces, allowing them to roll smoothly and evenly under load.
The tapering of the rollers creates a point of contact at the apex of the cone, which enhances load capacity and reduces friction. This unique design allows tapered thrust bearings to support heavy axial loads while simultaneously accommodating radial loads, making them versatile for various applications.
Functionality
The primary function of a tapered thrust bearing is to manage axial forces, which are loads that act parallel to the axis of rotation
. These bearings excel in applications where forces change direction or intensity, providing stability and reliability. Furthermore, their design allows for a high degree of efficiency and low operating temperature, which is crucial in high-speed machinery.tapered thrust bearing
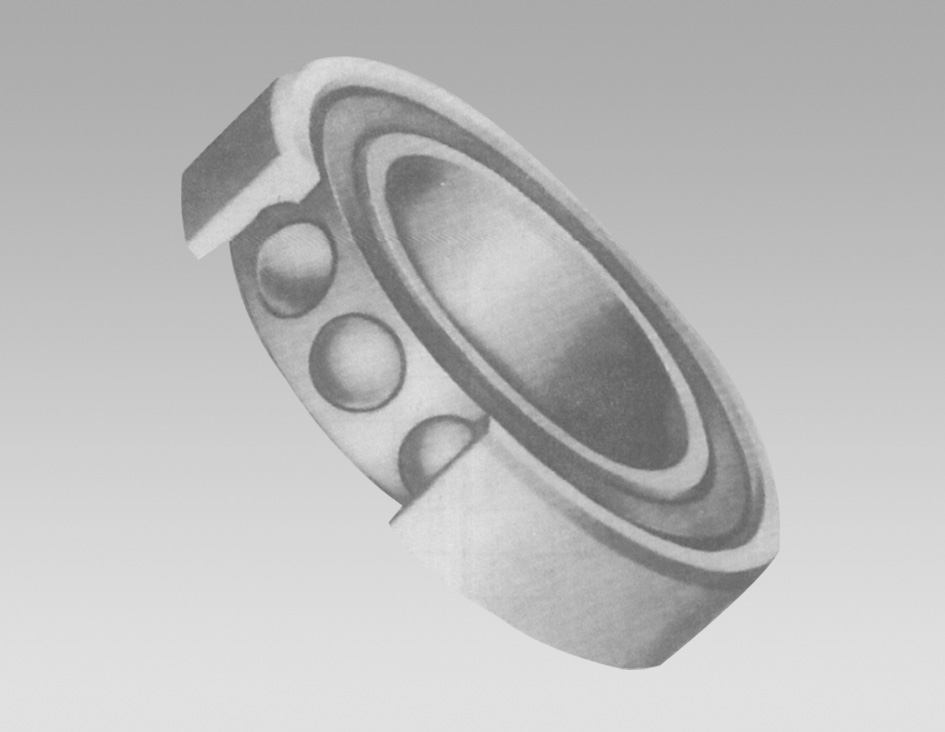
During operation, as the shaft rotates, the tapered rollers roll along the raceways, creating a smooth movement. This rolling action minimizes wear and tear on the bearing surfaces, extending the lifespan of the bearing and the machinery it supports. Tapered thrust bearings also have the capability to handle misalignment, which is particularly important in dynamic applications where parts may not always align perfectly.
Applications
Tapered thrust bearings are used extensively in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction. In automotive applications, they are commonly found in gearboxes, differential assemblies, and turbines, where they help manage the significant axial loads generated by these mechanisms.
In the aerospace sector, tapered thrust bearings are critical components of jet engines and landing gear systems, where reliability and performance are paramount. Their ability to support heavy loads while withstanding harsh environmental conditions makes them an ideal choice.
Construction machinery, such as cranes and excavators, also benefits from the use of tapered thrust bearings. These machines experience high levels of axial forces during operation, and tapered thrust bearings play a vital role in ensuring smooth and efficient functionality.
Conclusion
In summary, tapered thrust bearings serve an essential role in modern engineering by efficiently managing axial loads in a variety of applications. Their unique design, which combines tapered rollers and raceways, enables them to handle heavy loads while providing stability and reducing friction. As industries continue to advance and machinery becomes increasingly complex, the demand for reliable components like tapered thrust bearings will only grow. Understanding their design and applications is crucial for engineers and manufacturers looking to optimize performance and reliability in their systems.
Latest news
-
The Future of Deep Groove Ball Bearings For Extreme Applications
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Self-Lubricating Bearings: The Future of Agricultural Machinery Efficiency
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Nanotechnology in Ball Bearing Machines: The Future of Friction Reduction
NewsJul.31,2025
-
How Deep Groove Ball Bearings Are Tailored for Different Uses
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Energy-Efficient Machinery Bearings: Reducing Power Consumption in Large-Scale Ball Mills
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Deep Groove vs. Angular Contact: Which Ball Bearing Wins in High-Speed Applications
NewsJul.31,2025
