
Oct . 22, 2024 06:04 Back to list
Understanding the Functionality and Applications of Radial Thrust Ball Bearings in Machinery
Understanding Radial Thrust Ball Bearings Design, Function, and Applications
Radial thrust ball bearings are an essential component in various mechanical systems, providing support and stability for rotating elements. As the demand for more efficient machinery grows, understanding the design and functionality of these bearings becomes increasingly important for engineers, manufacturers, and maintenance professionals alike. In this article, we will explore the basic design principles of radial thrust ball bearings, their applications, advantages, and considerations for selection.
What are Radial Thrust Ball Bearings?
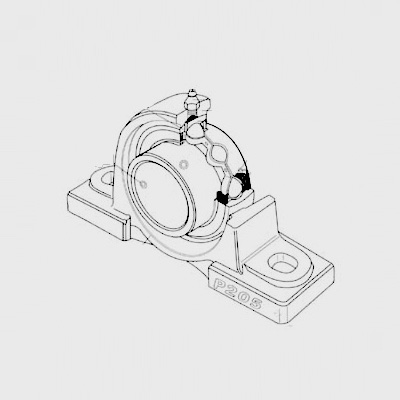
Radial thrust ball bearings are designed to handle both radial and axial loads. Unlike traditional radial ball bearings, which primarily manage radial forces, radial thrust ball bearings can accommodate forces acting on the shaft in a radial direction and axial direction simultaneously. These bearings consist of an inner and outer ring, a set of balls, and a cage, which separates the balls and maintains their alignment.
The unique design of radial thrust ball bearings allows them to support heavier axial loads while reducing friction. The balls form a point contact with the raceways, which minimizes surface contact area and, in turn, reduces wear and heat generation. This characteristic makes them ideal for applications that require stability and durability under varying load conditions.
Design and Construction
The construction of a typical radial thrust ball bearing involves a few key components
1. Inner Ring This part fits snugly onto the shaft, allowing it to rotate freely. 2. Outer Ring This ring is fixed in place within the bearing housing, providing a stable surface for the balls. 3. Balls These rolling elements are typically made from high-grade steel or ceramic materials to ensure durability and smooth operation. 4. Cage The cage acts as a separator, ensuring even distribution of the balls, thus reducing friction and preventing wear.
The precision with which these components are manufactured directly influences the performance and lifespan of the bearing.
Applications
Radial thrust ball bearings find applications across various industries. Some common uses include
- Automotive In cars, radial thrust ball bearings can be found in wheel hubs, gearboxes, and drive trains, where they reduce friction and enhance the efficiency of moving parts. - Industrial Machinery In manufacturing equipment, these bearings support rotating shafts, helping to stabilize equipment and ensure smooth operation, even under heavy loads. - Aerospace Aircraft engines utilize these bearings to maintain strict tolerances and reduce wear during high-speed operation, contributing to overall safety and efficiency. - Household Appliances Radial thrust ball bearings are also common in everyday appliances, such as washing machines and refrigerators, where they help to maintain functionality under continuous use.
radial thrust ball bearing
Advantages
1. High Load Capacity One of the most significant advantages of radial thrust ball bearings is their ability to handle high axial loads while maintaining radial load capacity.
2. Reduced Friction The design minimizes contact surface area, resulting in lower friction, which translates to less heat buildup and wear over time.
3. Durability Due to the materials and manufacturing processes employed, these bearings exhibit high wear resistance and can operate effectively for extended periods.
Considerations for Selection
When selecting radial thrust ball bearings for a specific application, several factors must be taken into account
- Load Requirements Understanding the types of loads that the bearing will be subjected to is crucial for ensuring optimal performance.
- Speed Bearings must be rated appropriately for the speed at which they will operate to prevent premature failure.
- Environmental Conditions Factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants can significantly impact the performance and longevity of the bearings.
- Lubrication Proper lubrication is essential for maintaining performance and reducing wear, which necessitates consideration of the working environment and bearing design.
Conclusion
Radial thrust ball bearings are vital components in modern machinery, offering versatile solutions for managing various loads. Understanding their design, function, and applications allows engineers and manufacturers to make informed decisions, ensuring the efficiency and reliability of their products. As technology continues to advance, the role of these bearings will only grow, highlighting the importance of ongoing education and innovation in this field.
Latest news
-
Premium Deep Groove Ball Bearings | High Speed & Reliability
NewsAug.29,2025
-
Durable Scaffolding Clamps - Secure & Reliable Tube Connectors
NewsAug.28,2025
-
Common Failures in Thrust Ball Bearings and Solutions
NewsAug.22,2025
-
How Tapered Roller Bearings Can Take Shock Loads
NewsAug.22,2025
-
Angular Bearings in High-Precision Spindles
NewsAug.22,2025
-
The Impact of Misalignment on Cylindrical Roller Bearing Performance
NewsAug.22,2025
