
Aug . 06, 2024 09:11 Back to list
Cross-sectional Analysis of Deep Groove Ball Bearings and Their Structural Characteristics
Understanding Deep Groove Ball Bearings A Cross-Sectional Analysis
Deep groove ball bearings are one of the most widely used types of rolling bearings in various mechanical applications. Their simple design, versatility, and ability to accommodate both radial and axial loads make them a popular choice in industries ranging from automotive to manufacturing. To appreciate the functionality and design intricacies of deep groove ball bearings, a thorough understanding of their cross-section is essential.
Design and Structure
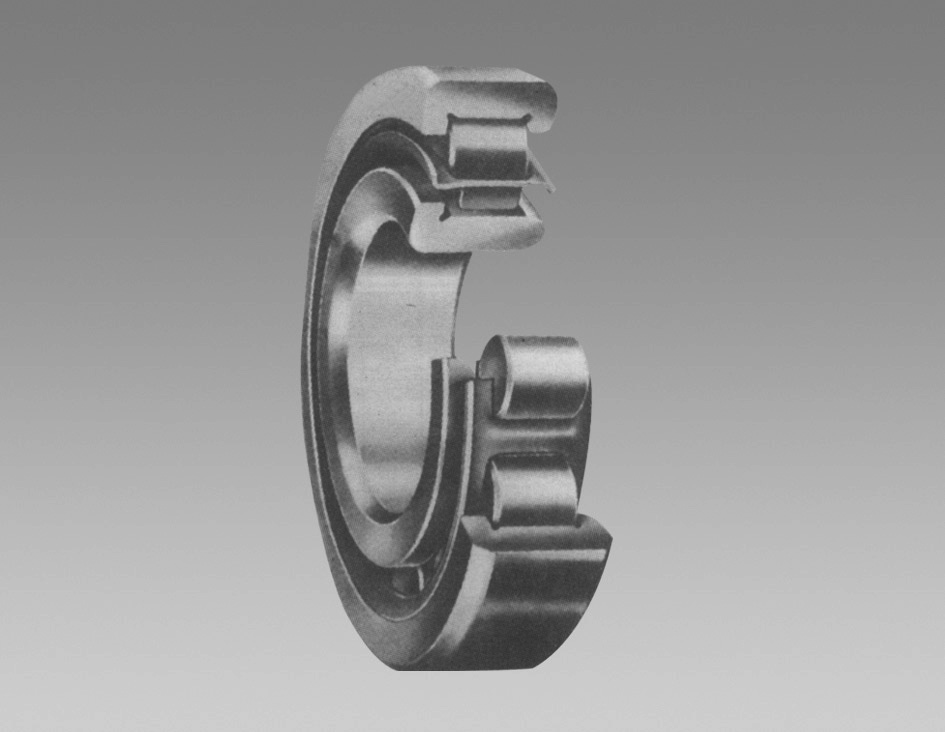
A typical deep groove ball bearing consists of an outer ring, an inner ring, a series of balls, and a cage (also known as a retainer or separator). The cross-section of a deep groove ball bearing reveals the arrangement of these components and provides insights into how they work together to facilitate smooth operation.
1. Outer Ring The outer ring is usually mounted in a housing. It has a deeper groove than the standard ball bearings, which allows for a greater number of balls and increased load capacity. The design also aids in minimizing stress and prolonging service life.
2. Inner Ring The inner ring fits onto the shaft and rotates with it. The design of the inner ring, like that of the outer ring, includes a groove that securely retains the balls, ensuring efficient load distribution and reducing friction.
3. Balls The rolling elements are typically made of steel or ceramic and are the crucial parts that facilitate the movement of the bearing. The deep groove design allows for a greater rolling surface area, thus enhancing load capacity and reducing wear over time.
4. Cage The cage separates the balls and maintains their proper spacing, enabling smooth and efficient motion. It also helps to keep the balls oriented correctly, reducing friction and vibration during rotation.
deep groove ball bearing cross section
Functional Characteristics
The deep groove configuration offers several advantages. It allows for accommodation of both radial and axial loads, which is particularly beneficial in applications where forces can act in multiple directions. The deeper groove also enables the bearing to cope with larger displacements and misalignments, thus improving reliability.
The smooth surface finish of deep groove ball bearings minimizes friction, which in turn reduces heat generation during operation. This quality is vital for applications that require high-speed operation, as excessive heat can lead to premature failure of the bearing.
Application Areas
Deep groove ball bearings find applications in a myriad of industries, including
- Automotive These bearings are commonly used in electric motors, gearboxes, and wheel hubs, where they contribute to the smooth operation of various vehicle components. - Industrial Machinery They are prevalent in conveyor systems, pumps, and motors, providing essential support in manufacturing processes. - Household Appliances From washing machines to vacuum cleaners, deep groove ball bearings are integral to the functionality of many everyday appliances.
Conclusion
The deep groove ball bearing stands as a testament to the advancements in engineering and design. Its cross-sectional structure reveals the careful consideration of load management, friction reduction, and reliability. As technology progresses and the demand for precision machinery grows, the significance of deep groove ball bearings in various industries is expected to increase further. Understanding their design and functionality not only highlights their importance but also underscores the continuous innovation within the field of mechanical engineering.
Latest news
-
Common Failures in Thrust Ball Bearings and Solutions
NewsAug.22,2025
-
How Tapered Roller Bearings Can Take Shock Loads
NewsAug.22,2025
-
Angular Bearings in High-Precision Spindles
NewsAug.22,2025
-
The Impact of Misalignment on Cylindrical Roller Bearing Performance
NewsAug.22,2025
-
The Role of Cage Design in Deep Groove Ball Bearing Durability
NewsAug.22,2025
-
The Impact of Material Quality on Machinery Bearings’ Lifespan
NewsAug.22,2025
