
Nov . 23, 2024 01:58 Back to list
angular contact ball bearing drawing
Understanding Angular Contact Ball Bearings Design and Applications
Angular contact ball bearings play a crucial role in various mechanical systems by supporting axial and radial loads simultaneously. Their unique design allows them to accommodate high speeds and provide high precision, making them ideal for applications ranging from industrial machinery to automotive components.
What are Angular Contact Ball Bearings?
Angular contact ball bearings consist of inner and outer rings, rolling elements (balls), and a cage that holds the balls in place. The key feature of these bearings is the raceways, which are angled relative to the axis of rotation. This angle, typically between 15° to 40°, allows the bearing to better handle axial loads in one direction while supporting radial loads.
The contact angle is significant because it determines the bearing's load capacity and its ability to withstand misalignment. Higher contact angles can accommodate heavier axial loads but may sacrifice some radial load capacity. In contrast, lower angles provide better radial load handling but can diminish axial load performance. Selecting the appropriate contact angle based on the application's requirements is essential for optimal performance.
Design Considerations
When designing or selecting an angular contact ball bearing, several factors need to be taken into account
1. Load Rating Understanding the dynamic and static load ratings of a bearing is crucial. Dynamic load rating refers to the bearing's ability to handle loads during motion, while static load rating pertains to the loads the bearing can withstand when at rest.
2. Speed Rating The maximum speed at which a bearing can operate effectively is determined by its design, materials, lubrication, and load conditions. Exceeding this speed can lead to excessive heat generation and premature failure.
3. Clearance and Fit The internal clearance of a bearing affects its performance. It can be adjusted to accommodate thermal expansion, lubrication conditions, and manufacturing tolerances. Additionally, the bearing's fit with other components (like shafts and housings) influences its operational efficiency and lifespan.
angular contact ball bearing drawing
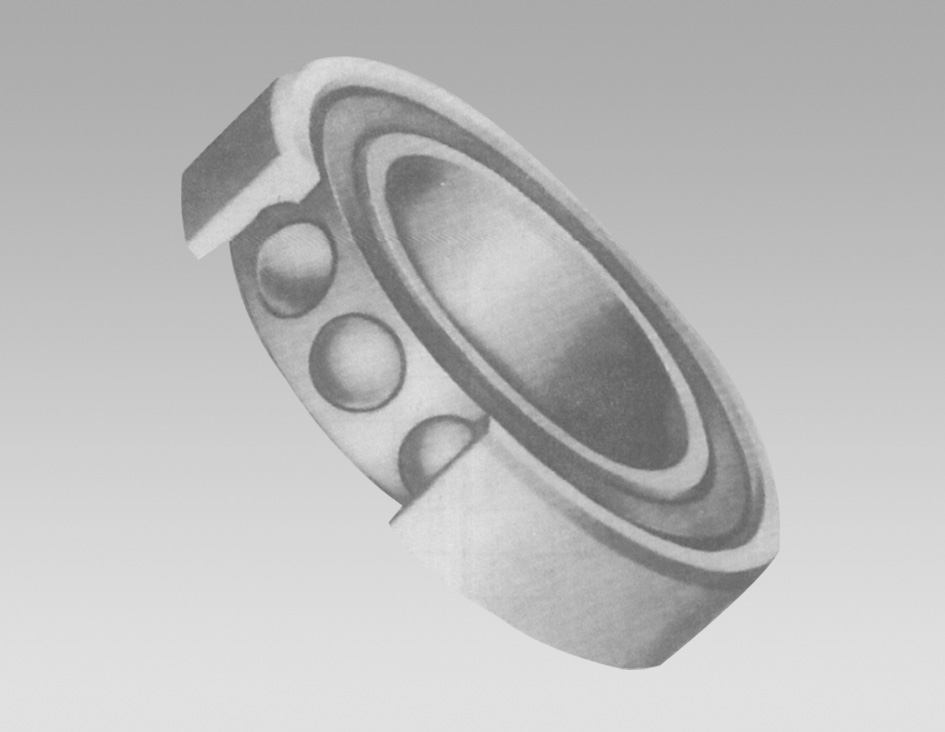
4. Material Selection Angular contact ball bearings are typically made from high-quality steel, but alternatives such as ceramic or hybrid materials may be used for specific applications to enhance wear resistance and reduce weight.
5. Lubrication Proper lubrication is vital for the longevity and efficiency of angular contact bearings. Options include grease or oil lubrication, and the choice depends on the operating environment and speed requirements.
Applications
Angular contact ball bearings are widely used in various industries due to their versatility. Common applications include
- Machine Tool Spindles In high-speed operations, such as milling and grinding, angular contact bearings provide the stability needed to maintain precision. - Electric Motors These bearings can handle the combined radial and axial loads found in motor applications, including fans and generators.
- Automotive Systems In vehicles, they are used in wheel hubs, transmissions, and differentials to support load and maintain smooth operation.
- Aerospace The lightweight and robust nature of angular contact bearings makes them suitable for applications like landing gear and fuel pumps.
Conclusion
Angular contact ball bearings offer a distinct advantage in applications requiring high-load capacity and precise movement. Understanding their design and selecting the appropriate type according to specific load conditions, speed, and lubrication can greatly enhance the performance and reliability of mechanical systems. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for precision-engineered components like angular contact ball bearings will only increase, solidifying their importance in modern engineering solutions.
Latest news
-
Premium Deep Groove Ball Bearings | High Speed & Reliability
NewsAug.29,2025
-
Durable Scaffolding Clamps - Secure & Reliable Tube Connectors
NewsAug.28,2025
-
Common Failures in Thrust Ball Bearings and Solutions
NewsAug.22,2025
-
How Tapered Roller Bearings Can Take Shock Loads
NewsAug.22,2025
-
Angular Bearings in High-Precision Spindles
NewsAug.22,2025
-
The Impact of Misalignment on Cylindrical Roller Bearing Performance
NewsAug.22,2025
