
Nov . 14, 2024 12:39 Back to list
angle contact ball bearing
Understanding Angle Contact Ball Bearings
Angle contact ball bearings play a crucial role in various mechanical applications, providing essential support and stability. These bearings are specifically designed to handle both radial and axial loads, making them versatile components in machinery where high precision and reliability are required. This article delves into the structure, functionality, applications, and advantages of angle contact ball bearings.
Structure and Design
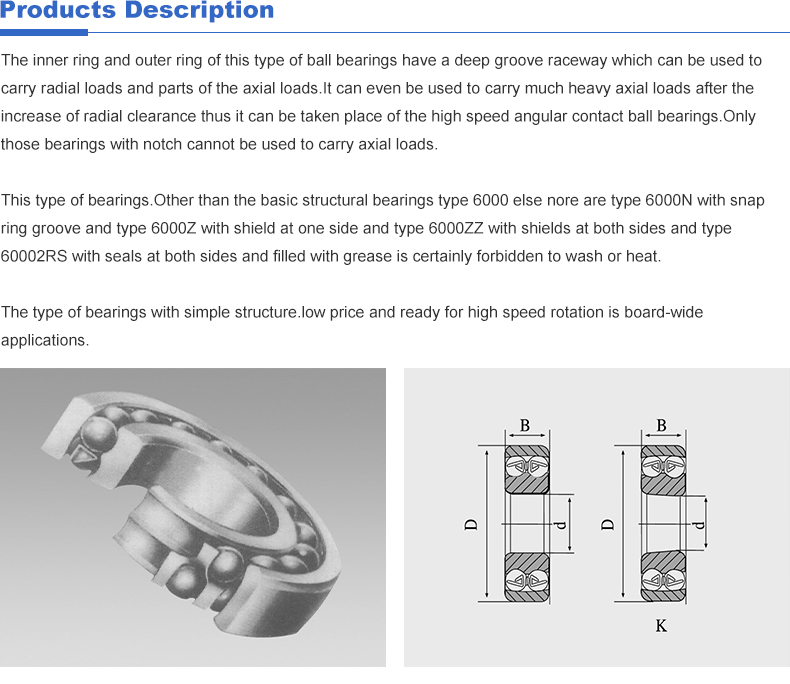
Angle contact ball bearings consist of two main components an inner ring and an outer ring, each equipped with a raceway. The most distinguishing feature of these bearings is their ability to accommodate loads at an angle, hence the name. The angle of contact typically ranges from 15 to 40 degrees, allowing the bearing to handle axial loads in one direction.
The design may vary depending on the type of application, with options for single-row and double-row configurations. The single-row bearings are suitable for applications where limited space is available, while double-row bearings can manage higher loads and provide increased stability. The balls within the bearing are positioned between the two rings, ensuring smooth rotation while maintaining the capacity to withstand forces applied on the axis.
Functionality
The primary function of angle contact ball bearings is to reduce friction between moving parts in machinery. This reduction in friction leads to an increase in efficiency, as less energy is wasted in overcoming resistance. The unique angle design allows these bearings to support both radial loads (those acting perpendicular to the axis of rotation) and axial loads (those parallel to the axis), making them ideal for applications such as motors, conveyors, and robotics.
Moreover, these bearings are capable of withstanding significant forces in high-speed applications. Their performance is enhanced by the materials used in construction—typically high-carbon chrome steel or ceramics—providing impressive durability and resistance to wear and tear.
Applications
angle contact ball bearing
Angle contact ball bearings are employed in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, robotics, and manufacturing. In the automotive industry, they are commonly found in electric motors, gearboxes, and wheel hubs, where they support critical components and ensure efficient operation. In aerospace, these bearings are used in landing gears and engine components, where reliability is paramount.
In robotic applications, angle contact ball bearings are crucial for precision movements, enabling robotic arms and joints to operate smoothly and accurately. Additionally, manufacturing machinery utilizes these bearings in CNC machines and lathes, where precision and load-bearing capacity are essential for maintaining the quality of the machined products.
Advantages
One of the primary advantages of angle contact ball bearings is their versatility. Their ability to handle both radial and axial loads makes them indispensable in various applications. Furthermore, their design allows for high-speed operation while minimizing noise and vibration, which is beneficial in environments where these factors could affect performance.
Another significant benefit is their ability to be preloaded. Preloading refers to the application of a specific load on the bearings even before operations begin. This technique reduces mechanical play and increases rigidity, enhancing the overall precision and stability of the system.
Lastly, the durability and longevity of angle contact ball bearings contribute to reduced maintenance costs and downtime. Their resistance to wear and fatigue, combined with proper lubrication, can lead to extended operational lifespans, ensuring that machinery runs efficiently over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, angle contact ball bearings are fundamental components that contribute to the efficiency and stability of various mechanical systems. Their unique design allows for the handling of both radial and axial loads, making them versatile across multiple industries. With applications ranging from automotive to aerospace, and the advantages of reduced friction, noise, and maintenance costs, angle contact ball bearings are integral to the advancement of modern engineering. As technology continues to evolve, the demand for such precision components will only increase, underscoring the importance of understanding and utilizing angle contact ball bearings in contemporary machinery.
Latest news
-
Premium Deep Groove Ball Bearings | High Speed & Reliability
NewsAug.29,2025
-
Durable Scaffolding Clamps - Secure & Reliable Tube Connectors
NewsAug.28,2025
-
Common Failures in Thrust Ball Bearings and Solutions
NewsAug.22,2025
-
How Tapered Roller Bearings Can Take Shock Loads
NewsAug.22,2025
-
Angular Bearings in High-Precision Spindles
NewsAug.22,2025
-
The Impact of Misalignment on Cylindrical Roller Bearing Performance
NewsAug.22,2025
