
Feb . 20, 2025 09:30 Back to list
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Cylindrical roller bearings play a pivotal role in modern engineering and industrial applications due to their robust performance and versatility. Understanding the different types of cylindrical roller bearings can significantly enhance system efficiency and longevity. This guide delves into the various types, emphasizing experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness to provide a comprehensive overview.
4. High-Capacity Cylindrical Roller Bearings Offering a combination of thin cross-sections and increased rolling elements, high-capacity bearings deliver excellent load handling even in compact machinery setups. These designs often implement advanced materials and technologies, reflecting significant expertise in minimizing weight while maximizing performance. In sectors such as aerospace and high-performance racing, the employability of high-capacity bearings underscores the industry's drive for innovation and efficiency. 5. Multi-Row Cylindrical Roller Bearings This configuration often involves two, three, or even four rows of cylindrical rollers, suitable for extremely heavy-duty applications. The increased number of rollers proportionally matches the demands of heavy machinery used in steel mills and paper manufacturing. Experts advocate for multi-row bearings where operational reliability is paramount because their design naturally accommodates axial expansion and radial loads without compromising structural integrity. Authority in Selection and Maintenance Selecting the appropriate type of cylindrical roller bearing necessitates a deep understanding of the machinery's operational environment and performance requirements. Engineers and technicians highly recommend adhering to industry standards (such as ISO and ANSI) to ensure compatibility and safety. Furthermore, authoritative sources underscore the significance of regular monitoring and maintenance. Ensuring correct installation, alignment, and lubrication effectively extends bearing life and enhances operational trustworthiness. Implementing condition monitoring technologies helps preemptively identify potential issues, establishing a proactive maintenance strategy. Conclusion Cylindrical roller bearings remain integral to the backbone of industrial machinery, with each type offering unique benefits tailored to specific applications. By leveraging expertise and maintaining comprehensive knowledge of each type's characteristics and use cases, engineers can significantly improve machinery efficiency and lifespan. Employing trusted sources and adhering to industry standards further solidifies the role of cylindrical roller bearings in modern engineering endeavors, reinforcing trust and reliability in every application.

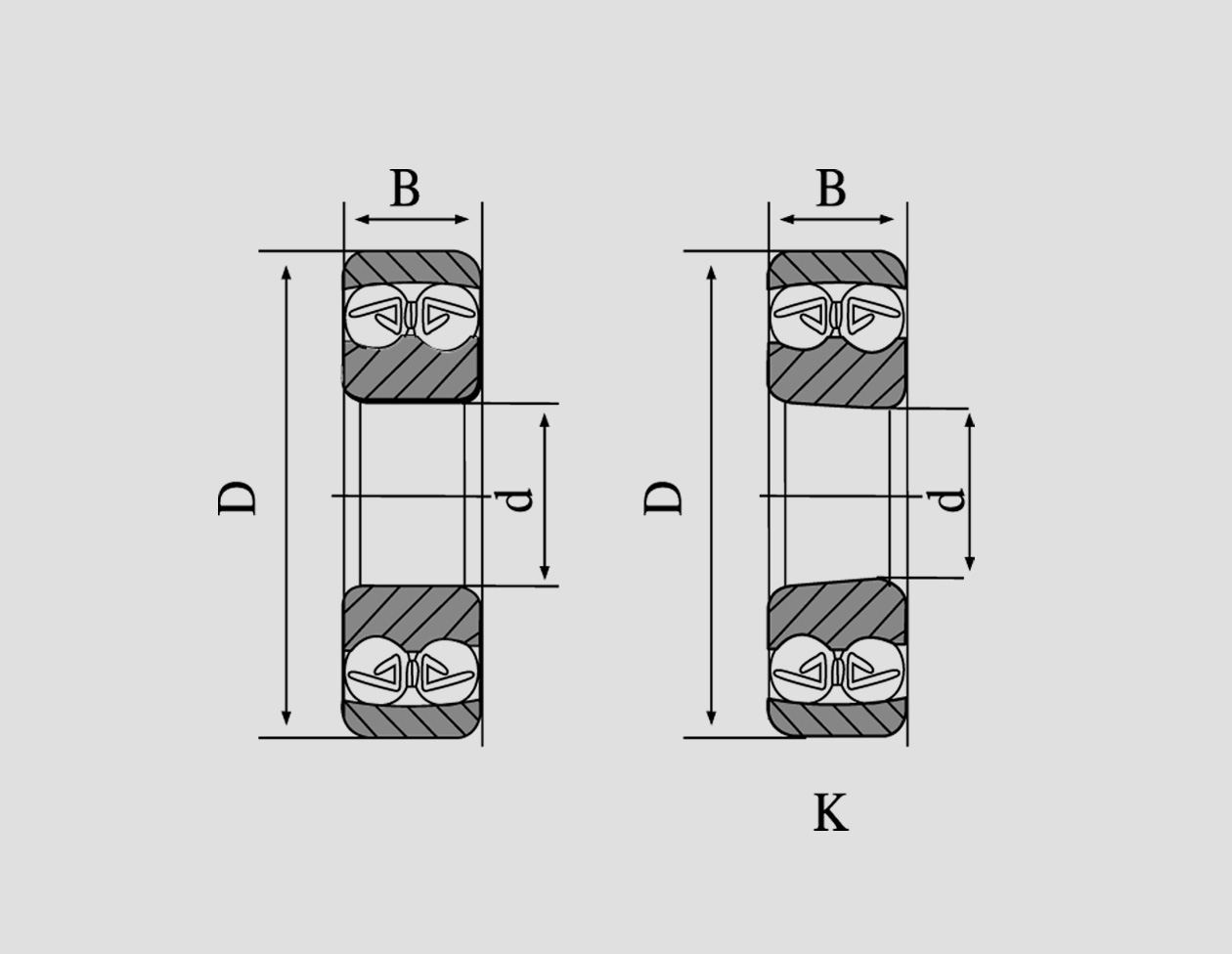
4. High-Capacity Cylindrical Roller Bearings Offering a combination of thin cross-sections and increased rolling elements, high-capacity bearings deliver excellent load handling even in compact machinery setups. These designs often implement advanced materials and technologies, reflecting significant expertise in minimizing weight while maximizing performance. In sectors such as aerospace and high-performance racing, the employability of high-capacity bearings underscores the industry's drive for innovation and efficiency. 5. Multi-Row Cylindrical Roller Bearings This configuration often involves two, three, or even four rows of cylindrical rollers, suitable for extremely heavy-duty applications. The increased number of rollers proportionally matches the demands of heavy machinery used in steel mills and paper manufacturing. Experts advocate for multi-row bearings where operational reliability is paramount because their design naturally accommodates axial expansion and radial loads without compromising structural integrity. Authority in Selection and Maintenance Selecting the appropriate type of cylindrical roller bearing necessitates a deep understanding of the machinery's operational environment and performance requirements. Engineers and technicians highly recommend adhering to industry standards (such as ISO and ANSI) to ensure compatibility and safety. Furthermore, authoritative sources underscore the significance of regular monitoring and maintenance. Ensuring correct installation, alignment, and lubrication effectively extends bearing life and enhances operational trustworthiness. Implementing condition monitoring technologies helps preemptively identify potential issues, establishing a proactive maintenance strategy. Conclusion Cylindrical roller bearings remain integral to the backbone of industrial machinery, with each type offering unique benefits tailored to specific applications. By leveraging expertise and maintaining comprehensive knowledge of each type's characteristics and use cases, engineers can significantly improve machinery efficiency and lifespan. Employing trusted sources and adhering to industry standards further solidifies the role of cylindrical roller bearings in modern engineering endeavors, reinforcing trust and reliability in every application.
Latest news
-
Grooved Ball Bearing Design and Functionality
NewsJun.04,2025
-
Concrete Mixer Bearing Load Capacity Testing
NewsJun.04,2025
-
6004 Bearing Dimensions in Robotic Joint Designs
NewsJun.04,2025
-
Advantages of Single-Row Deep Groove Ball Bearings
NewsJun.04,2025
-
Applications of Deep Groove Ball Bearings in Automotive Systems
NewsJun.04,2025
-
Innovations in Bearing Pressing Machine Design
NewsJun.04,2025
